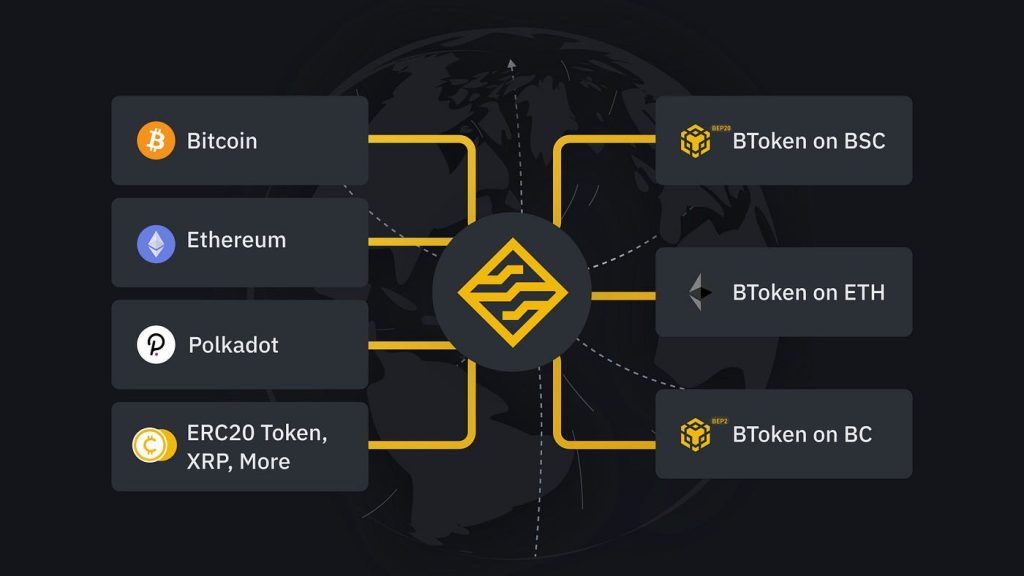
The BNB bridge is a network that connects the Binance Smart Chain (BSC) to the Ethereum blockchain, allowing assets and data to be transferred between the two networks. As two of the most popular blockchains in the crypto space, there is significant demand for interoperability between BSC and Ethereum. The BNB bridge aims to meet this need.
What is the BNB Bridge?
The BNB bridge is a cross-chain communication protocol created by the Binance cryptocurrency exchange. It utilizes a decentralized network of relayers to enable frictionless transfers of BEP-20 tokens between BSC and Ethereum. In essence, it provides liquidity between the two ecosystems while also facilitating composability for DeFi applications.
Some key capabilities of the BNB bridge include:
– Transfers of BEP-20 tokens to ERC-20 tokens and vice versa. Users can seamlessly move assets between BSC and Ethereum.
– Decentralized custody of assets using smart contracts. User funds have no central point of failure.
– High-speed transactions. Transfers across the bridge happen quickly thanks to BSC’s one-second block times.
– Low transaction fees. BSC’s low gas fees make bridge transfers affordable compared to transacting solely on Ethereum.
– Support for NFTs, data, and arbitrary logic. Not just asset transfers.
The BNB token plays a central role in the BNB bridge ecosystem. It is used to pay transaction fees and compensate the network of relayers providing security for the bridge.
Why Connect BSC and Ethereum?
There are several compelling reasons for building a bridge between BSC and Ethereum.
Firstly, it allows users to leverage the strengths of both networks. For example, applications can harness Ethereum’s maturity and network effects while also tapping into BSC’s faster speeds and lower costs.
Secondly, it enables liquidity flow between ecosystems. Assets represented on both chains can pool liquidity and users can chase arbitrage opportunities.
Third, it paves the way for multi-chain applications. The bridge enables composability between chains for sophisticated cross-chain dApps.
Finally, a bridge mitigates congestion issues on Ethereum. BSC provides excess capacity to absorb activity and user growth.
For these reasons, a bridge stands to be a win-win for both communities, decentralizing infrastructure between chains.
How Does the BNB Bridge Work?
There are four main components to the BNB bridge infrastructure:
1. Validators
2. Relayers
3. Router contracts
4. Pegged token contracts
Validators provide security guarantees for the bridge by storing state proofs on both chains. Relayers actively monitor the chains and propose state transitions. Router contracts process the logic for transfers, while pegged assets represent a 1:1 mapping between chains.
Transfers occur by locking up the original asset, minting a pegged version on the destination chain, and unlocking it there. Relayers facilitate the handover using the router contracts.
For instance, a user can send ETH to the router contract on Ethereum. This is locked up, and pegged BETH is minted on BSC. A relayer picks up the state change and triggers the BETH to be unlocked on BSC so the user can redeem it.
The process works trustlessly in both directions thanks to the validators and decentralized network of relayers.
BNB Bridge Fees
The BNB bridge charges a 0.1% transfer fee on all cross-chain swaps.
This fee has two purposes:
1. Compensates relayers for operation costs
2. Discourages spam transactions
0.075% goes towards subsidizing gas and operating expenses of relayers. The other 0.025% goes to the Peggy fee pool to fund continued bridge development.
The fee mechanics are handled automatically by the router contracts. Users only need to ensure they have a small buffer for BNB or ETH to pay for the transaction.
Current TVL and Volume
As of February 2023, the BNB bridge has:
– Over $1.5 billion in total value locked
– ~$8-15M in daily transaction volume
– 240+ independent relayers ensuring uptime
It facilitates transfers for a mix of stablecoins, utility assets, governance tokens, and more. Top assets include BUSD, USDC, BNB, ETH, and pegged versions representing over 80% of volume.
Adoption continues to accelerate driven by further outreach and integration into DeFi protocols on both chains.
Future Outlook
Development plans are underway focused on trustless bridging for arbitrary data and computational logic between chains. This sets the foundation for advanced cross-chain smart contracts.
Expect more layer 2 solutions like zkSync to onboard as they enable scalability through validiums and rollups. Enabling asset transfers between these layers expands the design space for scalable dApps.
Finally, with multi-chain emerging as a key trend, there is potential for the BNB bridge to expand support for additional chains like Polygon, Solana, Polkadot, and more.
This would turn BSC into a decentralized interoperability hub – a very compelling value proposition for the ecosystem moving forward. Multi-hop bridges and liquidity routing stand to enhance capital efficiency across fragmented DeFi networks.
Overall, the BNB bridge stands well-positioned to play a key role in the multi-chain future by bringing BSC and Ethereum closer together. Continued growth is on the horizon as more protocols plug into its infrastructure.