192.168.1.1 is a default IP address used by many router manufacturers to access their device’s settings and configurations. When you type this address into your web browser, it opens the router’s administration panel, allowing you to make various adjustments.
To log in as an admin, you’ll need to enter the default username and password provided by the manufacturer. Common defaults include “admin” for both the username and password, but this can vary depending on the brand and model of your router. It’s crucial to change these default credentials for security reasons once you’re logged in.
Once you’ve accessed the admin panel, you have control over a range of settings. You can manage your network’s security, set up a Wi-Fi password, configure port forwarding, and even monitor connected devices. Additionally, you can troubleshoot network issues and update the router’s firmware for improved performance and security.
Read also: 192.168.0.1 – Login Admin
192.168.1.1 IP Address
To reach the admin page, enter 192.168.1.1 into your web browser’s address bar, or simply click on the link provided below.
If you’re connected to the same network as your Wi-Fi router, your router’s admin IP address should correspond to your local IP address.
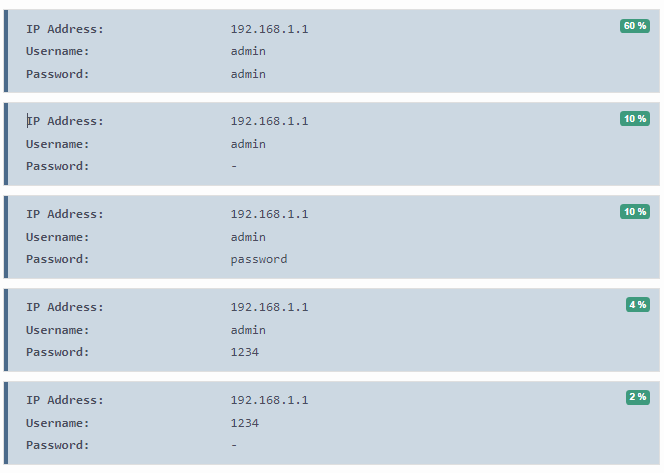
Default logins for 192.168.1.1
Login Steps
Accessing your router’s admin interface via the http://192.168.1.1 address grants you access to modify the settings and configurations provided by your router’s software. Be careful not to confuse this with http://192.168.l.l.
- To configure the router or make changes such as defining or altering the password, you’ll need to log in to the router’s admin. Simply input 192.168.1.1 into your browser’s address bar (URL bar).
- If an error message appears, it means that 192.168.l.l is not the correct IP address for your router. Manually type it in without relying on autocomplete, as it can sometimes lead to confusion. You can also refer to this article for guidance on identifying your router’s IP address.
- If you’ve forgotten your username and password, follow these instructions for recovery. If you haven’t changed the default login credentials provided with the router, consult our list of default router usernames and passwords.
Troubleshooting 192.168.1.1 or 192.168.l.l
In case you’ve forgotten your username and password, refer to these instructions for retrieval. If you haven’t altered the default login credentials provided with the router, you can find them in our list of default router usernames and passwords.
Connection – Ensure that the router is linked to your computer or other devices through either an ethernet cable or a WiFi connection. Take a moment to inspect all of the router’s indicator lights, including the Power, Internet, WiFi, and Ethernet lights.
Reboot – If your router is connected to a device, restart that device as well. Begin by unplugging both the router and modem, then reconnect them one by one after a brief pause. Wait for two minutes before checking again.
Firewalls – If you have a firewall in place, it’s crucial to temporarily disable it. Occasionally, a router may face difficulties accessing the internet due to conflicts with firewall settings.
Access via IP – Attempt to access the router console through your browser by entering the router’s IP address in the address bar. The correct address is 192.168.1.1, not 192.168.l.l. If these steps do not resolve the issue, you can perform a factory reset by pressing the reset button on the router.
192.168.1.1 IP Address And How To Use It
Are you making the most of your router’s capabilities? If you’ve been a frequent internet user, you’ve likely encountered a numerical representation like 192.168.1.1. This article provides an explanation of what 192.168.1.1 signifies and offers a fundamental guide on how to leverage it when accessing the internet.
What is 192.168.1.1?
This is often referred to as an online address. Every device connected to the internet is assigned a unique address, facilitating seamless data exchange between the device and the broader digital sphere. This concept parallels the distinctive postal addresses, email addresses, and telephone numbers we each possess for communication.
In the realm of the internet, this unique identifier is known as the Internet Protocol (IP) address. In a typical household network, the router takes on the responsibility of assigning an IP address to each connected device, including itself (router IP). A specific set of IP addresses has been set aside for private networks like homes, Local Area Networks (LAN), Wireless Area Networks (WAN) within businesses, and the like. These addresses are not applicable to publicly accessible websites on the internet. These designated ranges are as follows:
192.168.0.0 – 192.168.255.255
172.16.0.0-172.31.255.255
10.0.0.0- 10.255.255.255
An IP address is composed of four numbers, each ranging from 0 to 255. It consists of two main parts: the ‘Network Id’, encompassing the first three numbers, and the ‘device id’, which is the fourth number.
For instance, in the address 192.168.1.20, the network id is 192.168.1, while the device id is the final number, 20. In a home network with multiple connected devices, they will all share the same first three digits, indicating they belong to the same network. However, their unique identities are denoted by the differing fourth numbers. This is facilitated by the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) implemented on routers, allowing automatic assignment of distinct IPs to each device.
In addition to the private addresses for individual devices, there exists a public address for the network or router itself. All devices within a network share this common public address, which is visible to external networks.
During communication with an external network, the router translates private addresses into a public format. Conversely, when communicating with devices within its network, it converts public addresses back into their private equivalents. This process is known as Network Address Translation (NAT).
Popular with Linksys, D-link, Asus, Netgear, TP-Link
In the realm of home networks, a conventional choice for the router’s IP address is 192.168.1.1. This address serves as the default gateway or access point, acting as the primary conduit through which devices within the network communicate and connect to the broader online world. Due to this widespread convention, 192.168.1.1 is commonly referred to as the default gateway. This standardization simplifies access for everyday users, as they can easily recall this address to reach the router’s administrative console by inputting it into their browser’s address bar.
A multitude of popular router manufacturers adhere to this convention, such as D-link, Asus, Netgear, Cisco, Linksys, Tp-Link, Tenda, SMC Networks, Huawei, and Dell. Each router is accompanied by a manual that specifies the router’s unique IP address. This ensures users have easy access to their router’s settings and configurations.
Getting Connected
Before you begin configuring the router, ensure to follow these four crucial steps.
Verify Internet Connection: Check the functionality of the available internet connection by directly connecting the ethernet/ISP cable to a laptop or computer.
Unbox the Router: Typically, the router comes with a manual detailing its default gateway, username, and password. Place the router on a higher, central location for optimal coverage.
Power Up the Router: Allow some time for the router to boot up. Once ready for use, it will typically display a green indicator light or follow the indications outlined in the manual.
Connect the Router to the Internet Source: Attach the broadband cable/DSL modem/ISP gateway cable to the router’s designated internet port, which is often distinguished by a different color or noticeable placement.
Brands using 192.168.1.1
- 3 Com
- Abo Com
- Accton
- Acelink
- Actiontec
- Adb
- Adi Engineering
- Adtran
- Aerohive
- Airlink
- Airlink+
- Airlink101
- Airnet
- Alcatel
- Lucent
- Alfa Network
- Alice
- Allied Telesis
- Alpha
- Amigo
- Amrisc
FAQ: 192.168.l.l IP adddress
What is 192.168.1.1?
192.168.1.1 is a default IP address used by many router manufacturers to access their device’s settings and configurations.
How do I access the router admin using 192.168.1.1?
Open a web browser, type “http://192.168.1.1” into the address bar, and press Enter. Enter your username and password when prompted.
What if I can’t access 192.168.1.1?
Ensure you’re connected to the same network as the router. Check for typos and make sure there are no network issues. If problems persist, consult your router’s manual or manufacturer.
What are the default login credentials for 192.168.1.1?
Common defaults include “admin” for both the username and password, but these can vary by brand and model. Refer to your router’s manual or the manufacturer’s website.
Can I change the default IP address of my router?
Yes, it’s possible to change the router’s IP address, but it’s recommended to consult your router’s manual or seek guidance from the manufacturer to avoid network complications.
What can I do in the router admin panel?
In the admin panel, you can configure network settings, set up security measures, manage connected devices, and perform troubleshooting tasks.
Is it safe to change my router’s settings in the admin panel?
Yes, it’s safe to make changes, but be cautious. Avoid altering advanced settings unless you understand their implications. Always keep a record of any changes you make.
What do I do if I forget my router’s login credentials?
You can usually reset the router to its default settings, but this will erase any custom configurations. Consult your router’s manual or the manufacturer’s website for specific instructions.
Conclusion
IP address 192.168.1.1 is essential for managing router settings and configurations. This default gateway provides access to a plethora of options crucial for optimizing network performance and security. By following the recommended steps, users can effectively set up and configure their routers.
Additionally, being aware of common FAQs surrounding 192.168.1.1 ensures smooth troubleshooting and customization. Remember to exercise caution when making changes in the router admin panel, and always keep track of any modifications for future reference. With these insights, users can confidently navigate their network settings, ultimately enhancing their online experience.
